Yeast Calculator
Introduction
The Yeast Calculator is a comprehensive tool for homebrewers to calculate yeast requirements for fermentation. It helps determine how many yeast cells are needed for a brew, how much dry malt extract (DME) to use for starters, and projects yeast growth through multi-stage starters with different aeration methods.
This application is based on calculations derived from industry best practices and research by respected brewers including Chris White, Jamil Zainasheff, and Kai Troester.
Table of Contents
- User Interface Overview
- Using the Calculator
- Understanding the Calculations
- Advanced Techniques
- Troubleshooting
- References and Credits
- Download
User Interface Overview
The Yeast Calculator is organized into five main sections:
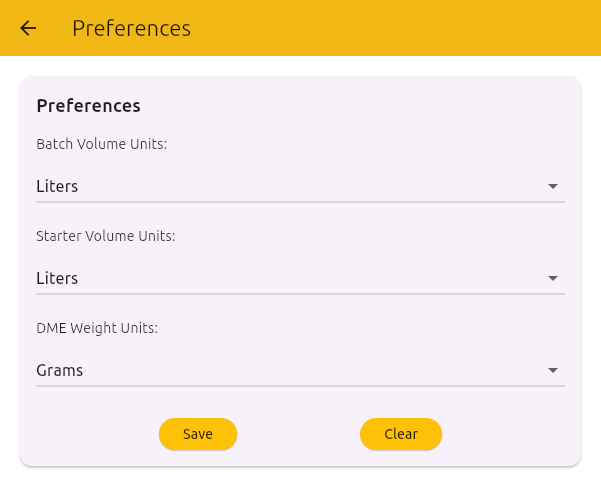
- Preferences - Set your measurement units and save preferences
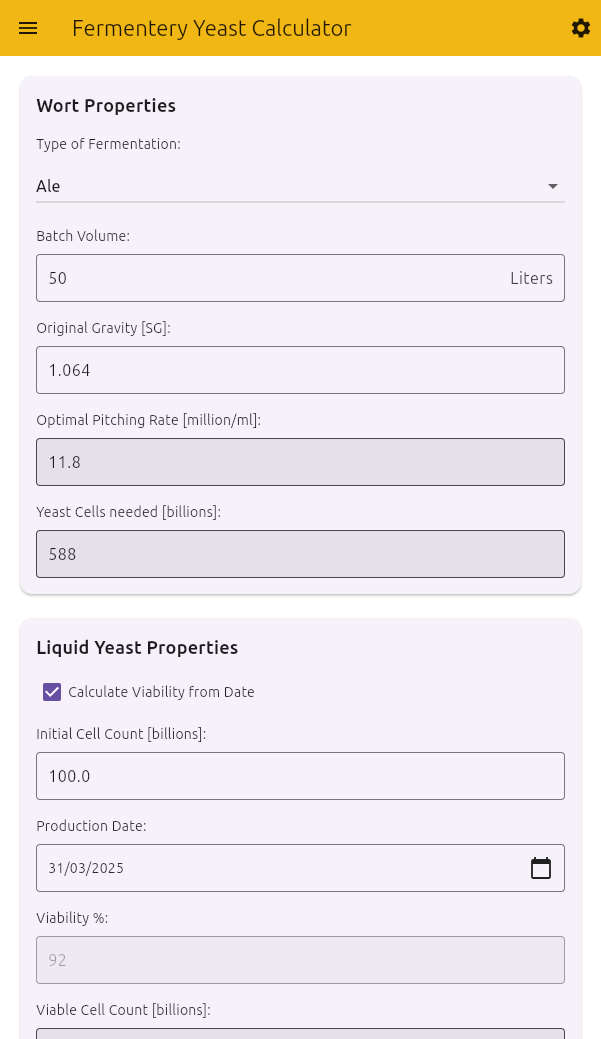
- Wort Properties - Enter details about your brew
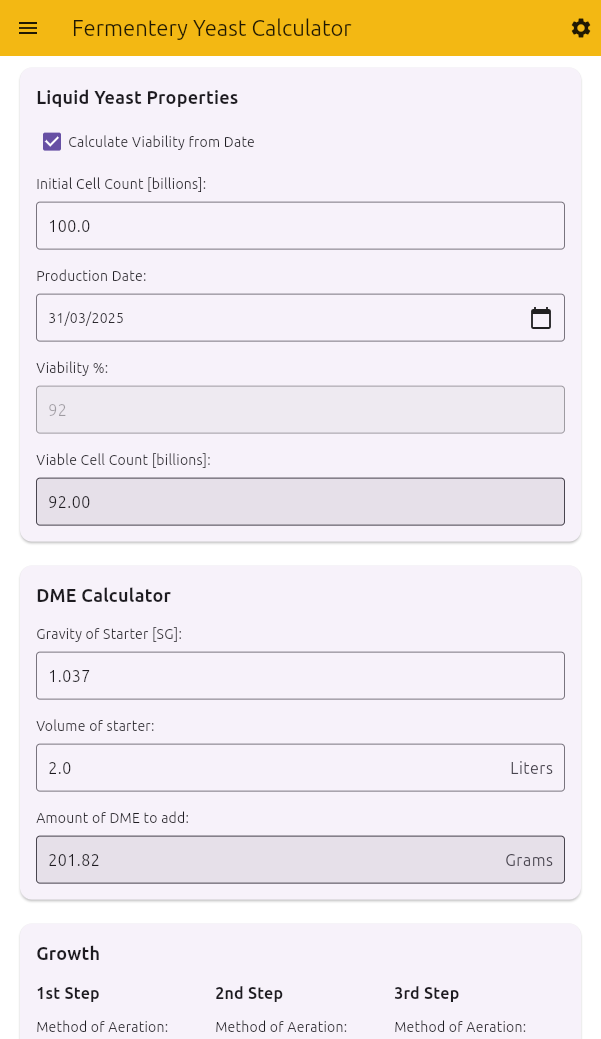
- Liquid Yeast Properties - Calculate viable yeast cells
- DME Calculator - Determine dry malt extract needed for starters
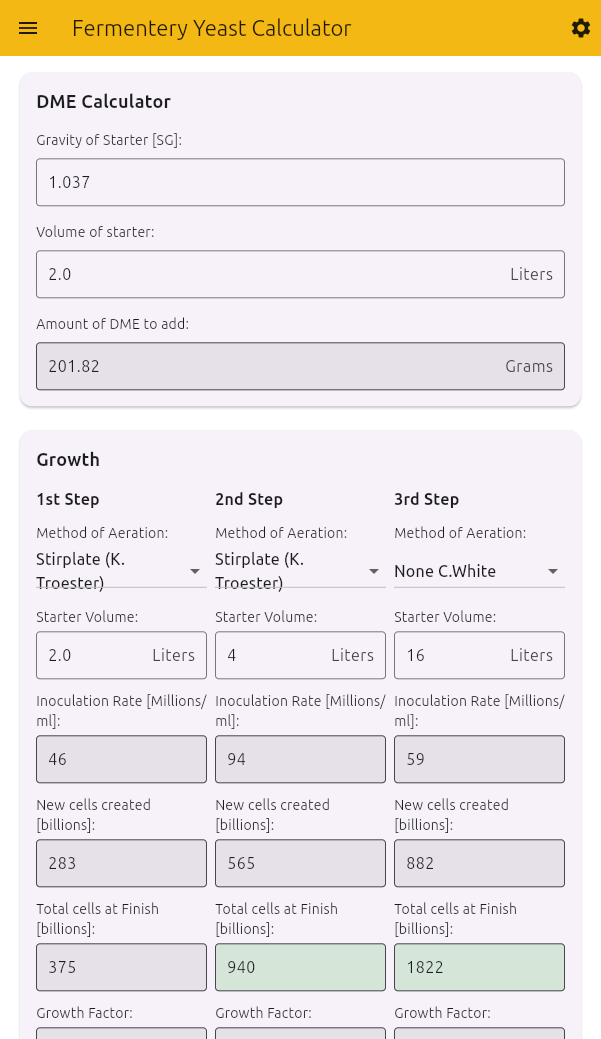
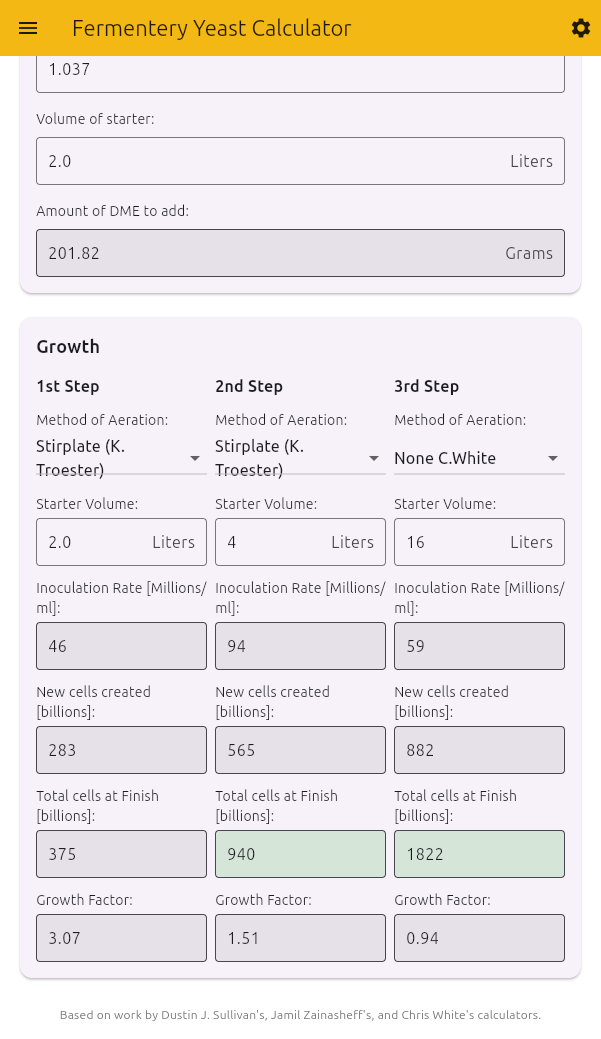
- Growth - Calculate yeast growth through up to three starter stages
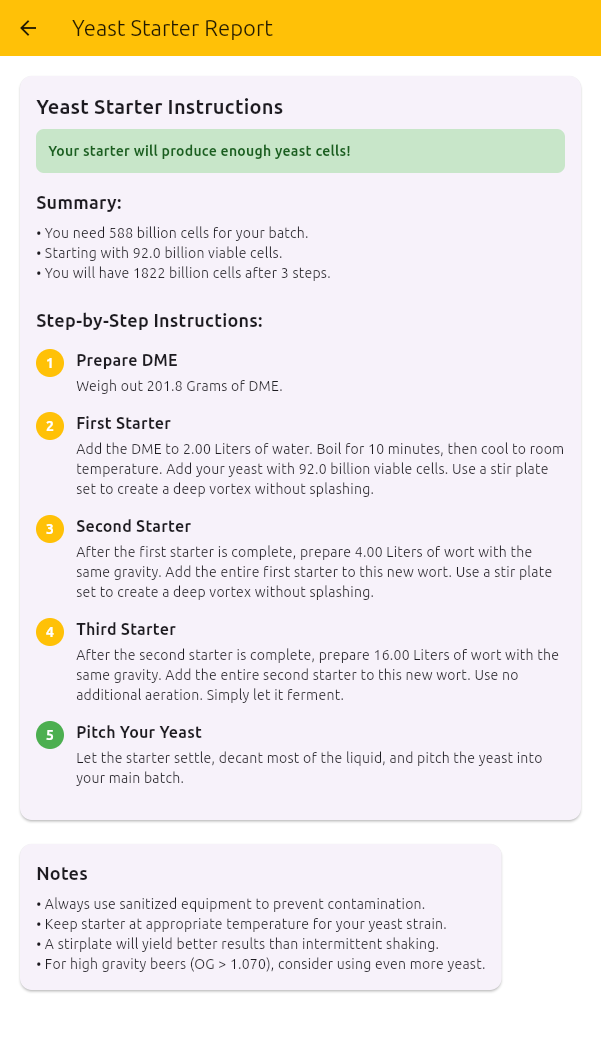
- Report - Show a step by step instruction for creating the starter
Each section is contained in a card with a clean, intuitive interface. The calculator automatically updates all results as you change inputs.
Using the Calculator
Preferences Section
This section allows you to set your preferred measurement units:
- Batch Volume Units: Choose between Litres and Gallons
- Starter Volume Units: Choose between Litres, ml, Gallons, and Quarts
- DME Weight Units: Choose between Grams and Ounces
Save and Clear buttons allow you to store and reset your preferences between sessions.
Wort Properties
Configure the details of your brew:
Type of Fermentation: Select between Ale, Hybrid, or Lager
- Ale: Uses a lower pitching rate (0.75 million cells/ml/°P)
- Hybrid: Uses a medium pitching rate (1.0 million cells/ml/°P)
- Lager: Uses a higher pitching rate (1.5 million cells/ml/°P)
Batch Volume: Enter your batch size in your preferred units
Original Gravity [SG]: Enter the specific gravity (e.g., 1.054)
The calculator will display:
- Optimal Pitching Rate: Target number of yeast cells per milliliter
- Yeast Cells needed: Total billions of cells required for your batch
Liquid Yeast Properties
Calculate viable yeast cells in your yeast package:
- Calculate Viability from Date: Toggle between date-based viability calculation and manual entry
- Initial Cell Count: Enter the total cell count in billions (typically 100 billion for a fresh vial/package)
- Production Date: If using date-based calculation, select the date of yeast production
- Viability %: The percentage of viable cells (calculated from date or manually entered)
The calculator displays:
- Viable Cell Count: The number of living yeast cells in billions
Note on Yeast Packages: White Labs vials and Wyeast smack packs typically contain approximately 100 billion cells when fresh. Dry yeast sachets typically contain much higher cell counts.
DME Calculator
Calculate how much dry malt extract you need for your starter:
- Gravity of Starter [SG]: The target gravity of your starter wort (typically 1.037-1.040)
- Volume of starter: The size of your starter in your chosen units
The calculator displays:
- Amount of DME to add: How much DME to use to reach your target gravity
Tip: A standard starter gravity is 1.037, which provides good growth without excessive stress on the yeast.
Growth Section
The Growth section simulates yeast growth through up to three stages, allowing for step-up starters:
For each step (1st, 2nd, and 3rd), configure:
Method of Aeration:
- None C.White: Basic starter with no special aeration
- Intermittent Shaking: Occasional shaking of the starter (Zainasheff method)
- Stirplate (J.Zainasheff): Continuous stirring with a stir plate (Zainasheff method)
- Stirplate (K. Troester): Continuous stirring with a stir plate (Troester method)
Starter Volume [Litres]: Size of that step’s starter
The calculator will display for each step:
- Inoculation Rate: The concentration of cells at the beginning
- New cells created: How many new billion cells will grow
- Total cells at Finish: The total billion cells after fermentation
- Growth Factor: The multiplication factor for the yeast
Note: When a step produces enough cells to reach the required total (as calculated in the Wort Properties section), the “Total cells at Finish” field will be highlighted in green.
Understanding the Calculations
Yeast Viability
For date-based viability, the calculator uses the formula:
Viability (%) = 97 * e^(-0.008 * days)
Where days is the number of days since the production date. This formula models the natural decline in yeast viability over time when stored refrigerated.
DME Requirements
The amount of DME required is calculated as:
DME (grams) = ((OG - 1) * 1000) * Volume(gallons) / 44 / 0.0022
This is based on the extract potential of typical DME, where 1 pound of DME in 1 gallon of water yields approximately 44 gravity points.
Cell Growth Models
Different cell growth models are used depending on the aeration method:
Basic Model (Used for all methods except Troester’s stirplate method):
Growth Factor = 12.518 * (Inoculation Rate^-0.458) New Cells = (Initial Cells * Growth Factor * Aeration Multiplier) - Initial CellsTroester Model (Used specifically for “Stirplate (K. Troester)” method): This model accounts for the relationship between DME amount and cell growth, with different calculations based on the cells-to-DME ratio.
Pitching Rate
The optimal pitching rate is calculated based on fermentation type and wort gravity:
Cells Needed = Volume(ml) * ((OG_Factor) * Type_Multiplier) / 1,000,000,000
Where:
- OG_Factor is derived from a polynomial equation that models the relationship between gravity and required cell density
- Type_Multiplier is 750,000 for Ales, 1,000,000 for Hybrids, and 1,500,000 for Lagers
Advanced Techniques
Multi-Stage Starters
For high-gravity beers requiring large yeast counts:
- Start with a smaller starter (1-2L)
- Let it fully ferment (typically 24-36 hours)
- Cold crash and decant the spent wort
- Add fresh wort at the volume specified in step 2
- If necessary, repeat for step 3
Yeast Harvesting
When harvesting yeast from a previous batch:
- Estimate the viable cell count based on the batch volume and expected yeast multiplication
- Use the Growth section to determine if additional growth is needed
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Unrealistic Growth Projections: Very high inoculation rates (>100 million/ml) can lead to inaccurate growth projections. Try using a larger starter or multi-stage approach.
Can’t Save Preferences: The app requires storage permission to save preferences. Check your app permissions.
Best Practices
- For most ales, aim for a pitching rate of 0.75 million cells/ml/°Plato
- For lagers, aim for a pitching rate of 1.5 million cells/ml/°Plato
- Keep the inoculation rate between 25-100 million cells/ml for optimal growth
- Cold-crash starters and decant spent wort before pitching to avoid potential off-flavors
References and Credits
- White Labs viability and growth rate research
- Jamil Zainasheff’s “Brewing Classic Styles” pitching rate guidelines
- Kai Troester’s stirplate growth model research
- Original Yeast Calculator by Dustin J. Sullivan
Download
Online Version (PWA enabled)
Android (apk)
- 2025-04-06: v0.1.0: yeastcalc.apk
Windows (setup)
- 2025-04-06: v0.1.0: yeastcalc-setup.zip
Linux (Appimage)
- 2025-04-06: v0.1.0 yeastcalc-latest-x86_64.AppImage